Calculating a riser is an essential skill for many fields, from stair design to plumbing and electrical systems. Understanding how to calculate riser height or size can help ensure safety, functionality, and code compliance in construction and system installation. But what exactly is a riser, and why is it so important to get it right? Whether you’re building a staircase, designing a plumbing system, or working on electrical installations, knowing how to accurately calculate riser measurements is a crucial step.
What is a Riser in Stair Design?
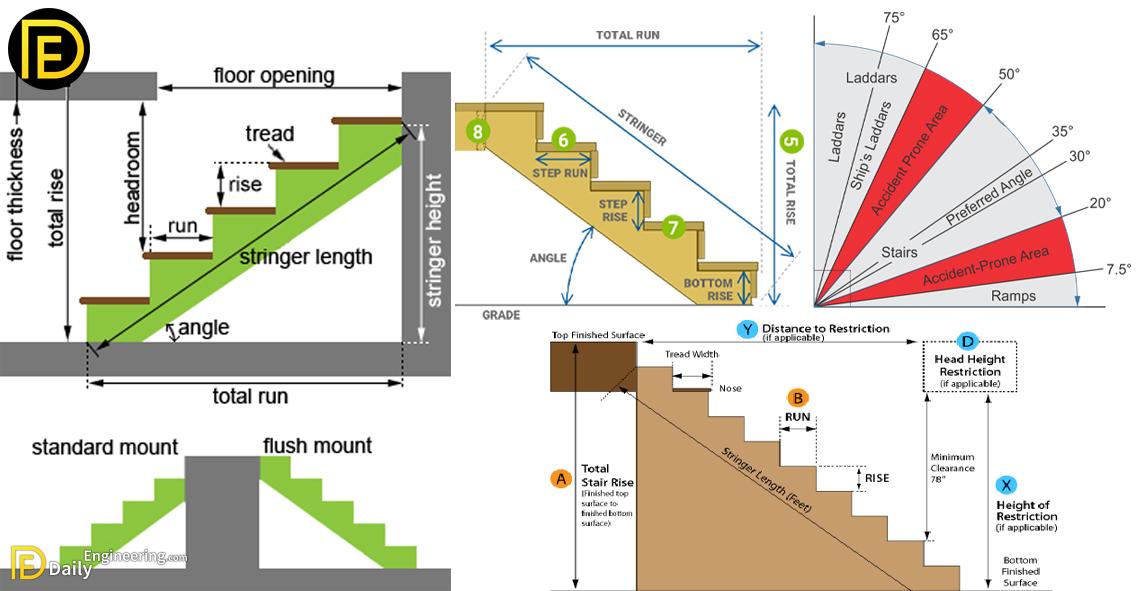
In the context of stair design, a riser is the vertical component of a staircase that connects one step to the next. It is the distance between the top of one step and the top of the next step. The riser height is a key factor in the comfort, safety, and overall usability of a staircase. If the riser is too high or too low, it can lead to discomfort or even accidents. Proper riser calculation ensures that people can use the stairs safely and efficiently.
Key Factors in Stair Design:
- Height of the Riser: Typically, the height of each riser should be between 7” to 8” (175mm to 200mm) for residential stairs. This range is considered comfortable for most users.
- Tread and Riser Ratio: The tread (the horizontal part of the step) and the riser should be in a balanced ratio. A common rule of thumb is the “17-inch rule,” which combines the tread and riser to give a total of 17-18 inches for a comfortable step. For example, a 7-inch riser usually pairs well with an 11-inch tread.
- Code Compliance: Many regions have specific codes regulating riser heights and tread widths to ensure safety. For example, the International Residential Code (IRC) in the U.S. states that the maximum riser height should not exceed 8.25 inches, and the minimum tread depth should be 9 inches.
What is a Riser in Plumbing?
In plumbing systems, a riser refers to the vertical pipe or tubing that carries water or wastewater to different levels of a building. Riser pipes are essential for maintaining water pressure and ensuring that plumbing systems function properly across multiple floors.
Key Considerations in Plumbing Riser Design:
- Water Supply Risers: These pipes bring water from the main supply to different parts of the building. Proper riser sizing is essential to ensure enough water pressure reaches every faucet or appliance.
- Wastewater Risers: Wastewater risers carry sewage and drainage water from various floors to the main sewer line. Proper sizing is necessary to prevent clogging and ensure effective drainage.
What is a Riser in Electrical Systems?
In the context of electrical systems, a riser refers to a vertical conduit or cable that carries electrical wiring between different floors of a building. These risers are crucial for ensuring that electricity is distributed safely and effectively to every part of the building.
Key Considerations in Electrical Riser Design:
- Riser Cable Sizing: The size of the riser cable depends on the load of electricity being carried, the number of floors in the building, and the type of electrical system. Oversized or undersized risers can lead to electrical hazards, such as overheating or inefficient power distribution.
- Code Requirements: Electrical risers must comply with national and local electrical codes, such as the National Electrical Code (NEC) in the U.S. These codes specify requirements for the type of wire, conduit, and other materials used in risers.
Why is Riser Calculation Important?
Once you understand what a riser is, it’s crucial to grasp why accurate riser calculation is so important. Whether you’re working on a staircase, plumbing system, or electrical installation, calculating risers correctly is necessary for ensuring the functionality, safety, and compliance of your project. Let’s explore why getting it right matters in each of these applications.
Ensuring Safety in Stair Design
The most direct impact of riser height calculation in stair design is on safety. If the riser height is too tall or too short, it can lead to accidents, discomfort, or even physical strain for those using the stairs.
Key Safety Considerations:
- Tripping Hazards: If the risers are inconsistent or too high, users may trip or stumble when ascending or descending the stairs. For example, a riser that is too tall can make climbing stairs unnecessarily tiring and increase the risk of falls.
- Comfort and Ergonomics: A staircase with poorly calculated riser heights may not feel natural to use. For instance, if risers are too low, users might have to take extra steps to reach the next level, which can lead to inefficient use of the stairs. Conversely, overly high risers can cause discomfort, especially for children, elderly individuals, or people with disabilities.
- Compliance with Building Codes: Building codes often specify maximum and minimum riser heights, typically between 7” and 8” in residential staircases. Adhering to these regulations ensures that the staircase meets safety standards and can be used by everyone comfortably.
By carefully calculating the riser height, you ensure the stairs are safe, comfortable, and ergonomic for all users.
Efficiency and Functionality in Plumbing Systems
In plumbing systems, risers are used to deliver water supply and remove waste across various levels of a building. Correctly calculating riser size in plumbing is essential for maintaining water pressure, flow, and effective drainage.
Important Considerations for Plumbing Riser Calculation:
- Water Pressure Maintenance: Improperly sized risers can cause a drop in water pressure, especially in taller buildings. A well-calculated riser ensures that each floor has adequate water pressure, preventing weak flow from taps, showers, or toilets.
- Prevention of Blockages: In waste systems, risers need to be large enough to accommodate the volume of water flowing through. Too narrow of a riser can cause blockages or inefficient drainage, which can lead to clogs or even sewage backup.
- Optimizing Water Distribution: Correct riser sizing ensures that water is efficiently distributed across all floors of a building, whether it’s for hot water supply, heating systems, or general plumbing. This is particularly important in multi-story buildings, where different floor elevations and demands must be factored in.
Proper plumbing riser calculation helps keep water flowing smoothly, maintaining efficiency and preventing costly plumbing issues down the road.
Electrical Safety and Code Compliance
Electrical risers, which carry electrical wires and cables from floor to floor, are crucial for ensuring that electricity is safely and effectively distributed throughout a building. Calculating the correct size of the electrical riser is essential for ensuring both safety and efficiency in the electrical system.
Why Accurate Riser Calculation Matters in Electrical Systems:
- Load Capacity: Riser cables need to be sized properly to handle the total electrical load of a building. Overloading risers can cause cables to overheat, leading to potential fires or equipment failure.
- Compliance with Electrical Codes: Electrical risers must adhere to local codes (e.g., the National Electrical Code in the U.S.) to ensure safety and prevent violations. These codes regulate the type, size, and installation methods for riser cables, helping avoid issues like improper wiring, overheating, or electrical hazards.
- Efficient Distribution of Power: If the riser is undersized, it can cause voltage drops, resulting in inefficient power distribution and even damage to electrical equipment. Proper calculation ensures that each floor receives adequate power without unnecessary losses.
Whether it’s maintaining safety or ensuring compliance with electrical codes, correct riser sizing is crucial for the reliable and safe operation of electrical systems in buildings.
By understanding the importance of riser calculation, you can ensure that your project—whether it’s a staircase, plumbing installation, or electrical system—functions as intended, is safe for use, and complies with relevant codes and regulations.
How to Calculate Riser for Stairs
Now that we understand the importance of riser calculation, it’s time to dive into how to calculate risers for stairs, which is one of the most common applications of this term. Calculating the correct riser height ensures that the staircase is safe, comfortable, and in compliance with building codes. Below, we’ll break down the steps and formulas involved in calculating risers for stairs.
Basic Formula for Riser Calculation
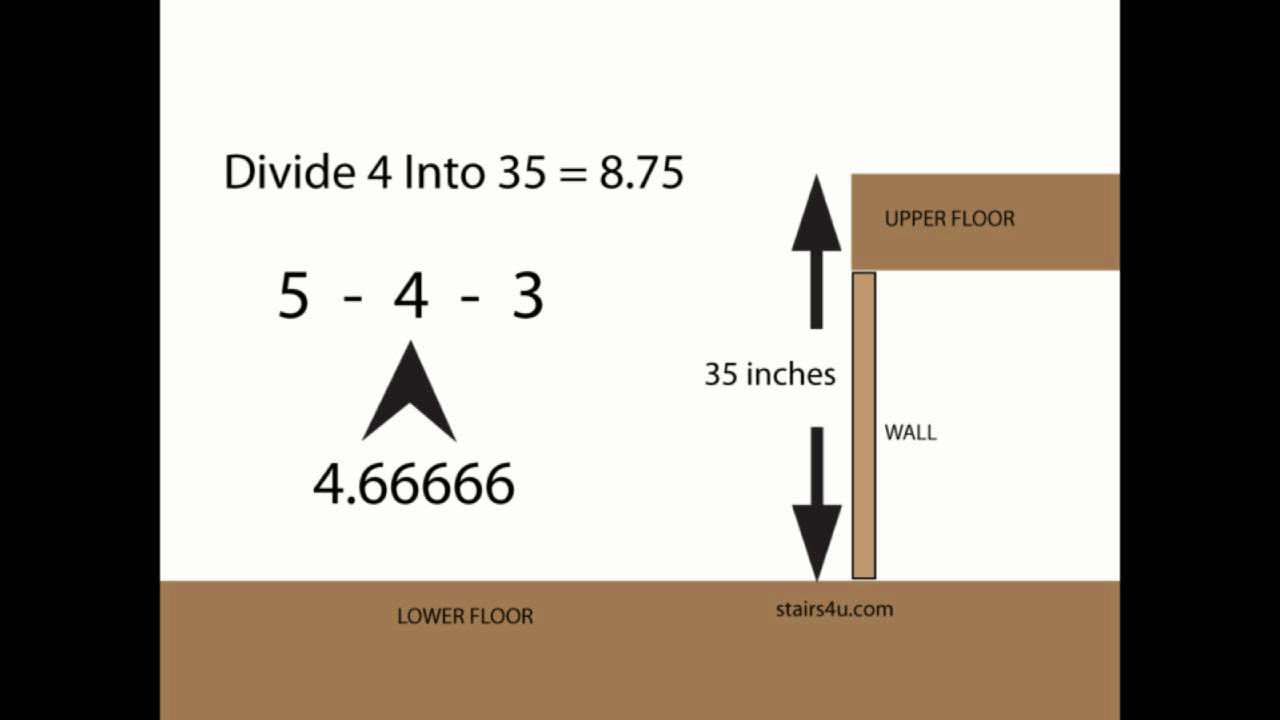
The basic formula for riser calculation in stair design is fairly straightforward. It involves dividing the total height between two floors (the floor-to-floor height) by the number of steps you want to have.
Formula:
Riser height=Total floor-to-floor heightNumber of steps\text{Riser height} = \frac{\text{Total floor-to-floor height}}{\text{Number of steps}}
For example, if the floor-to-floor height is 100 inches and you want to have 10 steps, the riser height would be:
Riser height=100 inches10=10 inches\text{Riser height} = \frac{100 \text{ inches}}{10} = 10 \text{ inches}
This formula is the most basic way of calculating risers for stairs, but it’s important to remember that the height should fall within the typical range of 7” to 8” (175mm to 200mm) for comfort and safety. If the riser height comes out to be higher than this, adjustments need to be made, either by changing the number of steps or adjusting the floor-to-floor height (if possible).
Riser Height Regulations
In most countries, there are specific building codes that regulate the maximum and minimum riser heights for staircases. This is done to ensure safety and comfort for users.
Typical Riser Height Regulations:
- Maximum Riser Height: Typically, the maximum allowable riser height is 8.25 inches (210mm) in residential buildings.
- Minimum Riser Height: On the lower end, the riser should generally not be less than 7 inches (175mm).
- Consistency: All risers on a staircase must be of uniform height. A single miscalculated riser can pose a serious safety hazard, leading to tripping or discomfort.
It’s important to consult local building codes before proceeding with riser calculations to ensure that your staircase is compliant with all relevant regulations. Local codes might have slight variations, but the principle of having a maximum and minimum height for risers remains consistent.
Calculating the Number of Steps
Once the riser height has been determined, the next step is to calculate how many steps you need to complete the staircase. This calculation depends on the floor-to-floor height and the desired riser height.
Formula:
Number of steps=Total floor-to-floor heightRiser height\text{Number of steps} = \frac{\text{Total floor-to-floor height}}{\text{Riser height}}
For example, if the total floor-to-floor height is 100 inches and you decide on a 7-inch riser height, you would calculate:
Number of steps=100 inches7 inches≈14.29\text{Number of steps} = \frac{100 \text{ inches}}{7 \text{ inches}} \approx 14.29
Since you can’t have a fraction of a step, you would round the number of steps to either 14 or 15, depending on the exact dimensions you choose. It’s important to note that rounding off the number of steps might slightly alter the final riser height, so make sure to adjust accordingly to maintain safe, consistent measurements.
Step Ratio (Riser vs Tread)
When designing stairs, the ratio between the riser and tread is crucial for ensuring comfort. The tread is the horizontal part of the step, where you place your foot, and the riser is the vertical part.
Ideal Riser and Tread Ratio: A common rule of thumb for a comfortable staircase is the 17-inch rule. This rule suggests that the sum of the riser height and tread depth should be between 17” and 18” (430mm to 460mm).
For example:
- If you have a 7-inch riser, you should aim for an 11-inch tread (7 + 11 = 18 inches).
- If you have an 8-inch riser, an 9-inch tread is typically recommended (8 + 9 = 17 inches).
This ratio helps ensure that the stairs are neither too steep nor too shallow. It strikes a balance between comfort and safety, allowing users to ascend and descend the stairs without too much effort.
Adjusting Riser Height for Sloped or Uneven Floors
In some cases, the floor-to-floor height is not perfectly level or is sloped, which can make riser calculations a bit more challenging. However, there are ways to adjust for uneven floors to ensure that the staircase is still safe and comfortable to use.
How to Adjust for Sloped or Uneven Floors:
- Measure the Rise at Several Points: If the floors are uneven, you may need to take multiple measurements at different points to calculate the overall rise accurately.
- Calculate the Average Riser Height: Once you have the measurements, calculate the average riser height by dividing the total rise by the number of steps.
- Adjust for Minor Differences: If there is only a slight difference in rise across the entire staircase, you may be able to adjust the riser height slightly at the top or bottom of the stairs to maintain consistency.
For more significant unevenness, you may need to make larger adjustments to the riser height or consider adding a small landing or step to level out the staircase. Always keep safety in mind when designing staircases on sloped or uneven floors.

How to Calculate Riser in Plumbing Systems
In addition to staircases, riser calculation is crucial in plumbing systems, particularly for vertical pipes that distribute water or carry wastewater throughout a building. Proper riser sizing ensures that water flows effectively, pressure remains consistent, and there are no drainage issues. Here, we’ll break down how to calculate risers for plumbing applications, including both water supply risers and waste risers.
Calculating Riser for Water Supply
The purpose of a water supply riser is to transport clean water from the main supply to the various floors of a building. It’s essential to calculate the correct size and pressure for the riser to ensure there’s adequate flow and pressure on every floor.
Factors Affecting Water Supply Riser Calculation:
- Flow Rate: The water flow rate required on each floor must be accounted for when calculating riser size. Higher flow rates require larger pipes to ensure that water can reach the upper floors without a drop in pressure.
- Pressure Requirements: In tall buildings, water pressure decreases as water travels upward. To counter this, riser pipes need to be adequately sized to ensure that water pressure remains sufficient on higher floors. This may involve the use of pressure-boosting systems, especially in high-rise buildings.
- Pipe Size: The size of the riser pipe depends on factors like the number of floors, the flow rate, and the type of fixtures connected to the riser. A larger building with more water outlets requires a larger riser pipe to handle the volume of water.
Example: Calculating the Water Supply Riser for a Multi-Story Building Suppose you have a 10-story building, and the total water flow required per floor is 50 gallons per minute (GPM). The pipe size must be calculated based on:
- Total flow demand
- Available water pressure at ground level
- Type of piping used (e.g., PVC, copper, etc.)
For simplicity, you can refer to standard plumbing codes, like the National Standard Plumbing Code (NSPC) or the Uniform Plumbing Code (UPC), which provide charts and guidelines for determining the appropriate pipe size for different water flow rates.
Calculating Riser for Wastewater Systems
A wastewater riser or drain riser carries sewage and wastewater from the upper floors down to the building’s main sewer line. Correct riser sizing is essential to avoid clogs, prevent backups, and ensure smooth waste flow.
Factors Affecting Wastewater Riser Calculation:
- Flow Rate of Wastewater: The flow rate depends on the number of fixtures (toilets, sinks, bathtubs, etc.) on each floor. Larger buildings with more plumbing fixtures will require a larger pipe to carry the wastewater.
- Pipe Size: Wastewater risers typically use larger pipes than water supply risers because the volume of wastewater is higher and the flow is more variable. Common sizes range from 4 inches to 6 inches in diameter, depending on the building’s size and the number of fixtures.
- Gravity and Slope: Unlike water supply risers, wastewater risers rely on gravity to carry waste downward. The pipe must be installed at a slight slope (usually 1/4 inch per foot) to encourage smooth drainage. If the riser is too steep, it could cause waste to move too quickly, potentially leading to blockages. If it’s too shallow, it can result in slow drainage and clogs.
- Ventilation: Proper ventilation of wastewater risers is important to avoid the buildup of gases like methane. Adequate venting ensures air can flow through the system and prevents pressure imbalances that could cause drainage issues.
Example: Wastewater Riser Calculation In a 5-story building with 3 toilets per floor and various other fixtures, you would first calculate the total fixture units (a standard measurement used in plumbing) for each floor. Using plumbing code tables, you can then select the appropriate riser pipe size and slope to accommodate the flow.
General Guidelines for Plumbing Riser Calculations
While the specific calculations depend on the building size and system requirements, the following general guidelines can help with riser calculations in plumbing systems:
- Determine the Flow Requirements: Identify the flow rate needed for each floor (e.g., for water supply or wastewater).
- Check Local Codes: Always consult the local plumbing code (such as the UPC or NSPC) for specific pipe sizing charts.
- Consider the Building Height: The taller the building, the more pressure and flow capacity you will need to account for in the riser.
- Use the Correct Pipe Materials: Make sure you select appropriate pipe materials that can handle the pressures and flow requirements of the riser. Materials like PVC, copper, and cast iron are commonly used in plumbing risers.
By following these guidelines, you can properly calculate and install plumbing risers that ensure a functional, safe, and efficient plumbing system for multi-story buildings.
How to Calculate Riser in Electrical Systems
Similar to plumbing risers, electrical risers carry electrical cables or conduits between different floors of a building. Correct calculation and installation of electrical risers are crucial to ensuring safe power distribution, minimizing energy loss, and complying with electrical codes. Let’s explore how to calculate electrical risers.
Determining the Electrical Load
The first step in calculating an electrical riser is determining the load that will be carried through the riser. The electrical load is the total amount of power (measured in amps) required by all the electrical outlets, lights, and appliances on each floor.
Steps to Calculate the Electrical Load:
- Identify Electrical Fixtures: Determine the total number of electrical fixtures (lights, outlets, appliances, HVAC systems) on each floor.
- Calculate Total Power Requirement: For each fixture, calculate the power consumption (in watts) and convert it to amperage (amps) by dividing by the voltage (typically 120V or 240V in residential and commercial settings).
- Sum the Loads: Add up the total amperage requirement for all floors to determine the overall load on the riser.
Choosing the Right Riser Cable
Once you have the electrical load, the next step is selecting the right riser cable. The cable size must be large enough to handle the calculated load without overheating. Electrical riser cables must also comply with local codes, such as the National Electrical Code (NEC) in the U.S.
Factors to Consider:
- Ampacity: The cable’s ampacity (its maximum current-carrying capacity) must be higher than the total load to ensure safe operation.
- Voltage Drop: Over long distances, voltage drops can occur, so it’s essential to choose the correct wire size to minimize this effect.
- Conduit Size: The conduit used to house the riser cable must also be sized appropriately to allow for easy cable installation and to prevent overheating.
Electrical Riser Safety and Compliance
When designing electrical risers, safety is paramount. Electrical risers should be installed by licensed electricians and comply with all relevant safety codes.
Safety Considerations:
- Overcurrent Protection: Install circuit breakers or fuses to protect against overloads.
- Fire Resistance: Use fire-resistant cables and ensure that the riser is routed through safe, non-combustible pathways.
- Proper Grounding: Ground the electrical riser properly to prevent electrical shocks or short circuits.