Riser measurement plays a crucial role in various industries, from construction to plumbing, HVAC systems, and electrical setups. Whether you’re a professional working on large-scale construction projects or a DIY enthusiast dealing with home improvements, understanding what riser measurement is and how to measure it accurately can save time, money, and effort. But what exactly is riser measurement? And why is it so important?
What Is a Riser?
A riser is typically a vertical or near-vertical pipe, duct, cable, or similar structure used in buildings and systems to transport fluids, gases, or electricity from one floor or level to another. They are essential in plumbing, electrical, HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems, and other infrastructure systems in buildings.
- Plumbing risers are used to carry water and waste systems vertically through buildings.
- Electrical risers are used to carry electrical cables between floors.
- HVAC risers are used to carry air ducts or ventilation systems throughout multi-story buildings.
In the simplest terms, a riser can be defined as any component that facilitates the upward or downward movement of materials or energy in a system. The measurement of these risers is crucial for proper system installation, efficiency, and safety.
Why Riser Measurement Matters
Accurate riser measurement is essential for a number of reasons:
- Space Utilization: Precise measurements ensure that the space available for risers is maximized, avoiding the need for costly adjustments or rework.
- System Efficiency: Riser size, height, and placement can directly impact the efficiency of plumbing, electrical, and HVAC systems. Incorrect riser measurements could result in poor performance.
- Safety: Improper riser measurements can lead to malfunctions, leaks, or electrical issues, all of which can compromise the safety of the structure.
- Cost Savings: By measuring risers accurately, you reduce the chances of unnecessary material waste or the need for modifications later in the construction or installation process.
For example, when installing a plumbing riser, if the height or diameter is miscalculated, it could lead to incorrect water pressure, pipe failure, or even flooding. Similarly, electrical risers that are too small could cause overheating and ultimately, fire hazards. Thus, riser measurement is not something to overlook.
Key Factors Involved in Riser Measurement
When measuring a riser, there are several key factors to consider. These will vary slightly depending on whether you’re measuring for plumbing, electrical, or HVAC systems. However, the basic principles remain the same.
The Dimensions of a Riser
There are several dimensions to consider when measuring a riser. These include:
- Height: The height of the riser is typically the most critical measurement. It determines how far the riser travels vertically through the building, and it affects the distribution of water, air, or electricity. To measure height, use a tape measure or a laser level to determine the distance between the base and the top of the riser.
- Diameter (or Width): This measurement is essential, especially for pipes and ducts, as it influences the flow rate. Larger diameters allow for greater flow, whether it’s water, air, or electrical wiring. When measuring diameter, use a caliper or a measuring tape for precision.
- Length: If the riser is horizontal at any point (for example, in HVAC systems), you’ll also need to measure its length. This ensures that the components fit properly into the designated space.
- Spacing: Riser spacing refers to the distance between multiple risers, if applicable. For example, when setting up a plumbing or electrical riser system, you’ll need to calculate the correct spacing to prevent interference between systems and allow for proper air or water flow.
Tools and Equipment for Riser Measurement
To get accurate measurements, it’s important to use the right tools for the job. Here are some tools commonly used for riser measurement:
- Tape Measure: The most basic tool for measuring height and length. Use it for basic riser measurements in both horizontal and vertical orientations.
- Laser Measure: A more advanced tool, especially useful for long distances. It provides accurate readings without the need for physical contact.
- Caliper: For precise measurement of diameter, especially when working with pipes or other round risers.
- Ruler or Square: For checking alignment and ensuring your riser measurements are even and straight.
- Plumb Line: Used to check vertical alignment, ensuring the riser is perfectly upright.
Choosing the right tool depends on the scale of the riser and the precision required. For example, measuring a plumbing riser that runs several floors may require a laser measure to ensure accuracy over long distances.
How to Measure a Riser: Step-by-Step Guide
Now that you understand the basics of riser measurement, let’s dive into how to actually measure a riser. The process can be broken down into a few simple steps.
Preparing for Riser Measurement
Before you begin measuring, you’ll want to gather all the necessary tools and ensure safety protocols are in place:
- Safety First: Ensure that you’re working in a safe environment. If you’re measuring an electrical riser, make sure the power is turned off. If measuring plumbing or HVAC risers, check that no fluid or air is running through the system.
- Check the Plan: Review the design or blueprint for the riser system to ensure you know exactly where the riser should be located and how much space it requires.
- Clear the Area: Make sure the area around the riser is clear of debris or obstacles that could obstruct your measurements.
Step-by-Step Riser Measurement Process
- Measure the Height:
- Use a tape measure or laser level to measure the vertical distance the riser will cover.
- Measure from the base (or floor) to the top (or ceiling) of the riser.
- For accuracy, double-check measurements at multiple points along the riser’s path, particularly if the surface isn’t perfectly straight.
- Measure the Diameter/Width:
- Use a caliper to measure the diameter of the pipe or duct if applicable.
- If you’re working with a flexible material, be sure to measure at multiple points to ensure consistency.
- Measure the Length (if applicable):
- If the riser includes horizontal runs, measure the length of these sections using a tape measure or laser tool.
- Ensure that horizontal risers maintain the correct slope if needed (for plumbing systems).
- Calculate the Spacing:
- If you’re working with multiple risers, measure the distance between them to prevent interference. This is especially important in plumbing and electrical systems where risers are placed next to one another.
Tips for Accurate Riser Measurement
- Use a helper: If the riser is very tall or difficult to access, a second person can help with holding tools or ensuring measurements are correct.
- Double-check your measurements: Always measure at least twice to ensure accuracy. Mistakes in riser measurements can lead to costly adjustments later.
Common Riser Measurement Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Even experienced professionals can make mistakes when measuring risers. These errors can lead to significant issues during installation, potentially compromising safety, efficiency, and even costing more time and money to fix.
Overlooking Important Dimensions
One of the most frequent mistakes is neglecting to measure all the relevant dimensions of a riser. For example, it’s easy to focus solely on the height of a riser and forget to measure its diameter or spacing between multiple risers. These dimensions are essential to ensure that the riser will function correctly in its intended system.
- Solution: Always take note of all measurements before starting installation. For example, when measuring a plumbing riser, you must measure both the height (vertical distance) and diameter (which affects water flow) to ensure the pipes fit properly and maintain adequate water pressure.
Using Incorrect Tools
Another mistake is using the wrong tool for the job. While a basic tape measure may be fine for most projects, complex systems like electrical risers may require more precise tools like calipers for diameter or laser distance measuring devices for vertical and horizontal runs.
- Solution: Always use the right tool for the specific type of riser you’re measuring. A laser measuring tool is ideal for tall, hard-to-reach vertical risers, while a caliper is essential when you need to measure the diameter of pipes with high accuracy.
Ignoring Alignment and Verticality
When measuring a riser, particularly for vertical systems, it’s essential to check for alignment. A riser that is slightly off vertical can lead to misalignment in the system, affecting the flow of materials or energy.
- Solution: Use a plumb line or a spirit level to ensure your riser is perfectly vertical. This is especially important in plumbing and electrical risers, where small deviations can cause long-term issues.
Failing to Account for Expansion and Contraction
Some materials, such as metal pipes or ducts, can expand or contract with changes in temperature. If this factor isn’t taken into account when measuring, the riser may not fit correctly once installed, or it could lead to stress on the system over time.
- Solution: Always account for the material’s expansion and contraction when designing riser systems. In plumbing, electrical, or HVAC systems, consult with manufacturer specifications for allowable thermal expansion of materials used in the riser system.
Inconsistent Measuring Method
Using inconsistent measuring techniques—like mixing imperial and metric systems—can lead to errors in measurement, especially in larger-scale projects. This is a particularly common mistake in international projects where different standards may apply.
- Solution: Stick to one system of measurement (either imperial or metric) throughout the entire project. If you’re working on a project that requires a combination of both, double-check your conversions to avoid inaccuracies.
Riser Measurement in Different Industries
Riser measurement plays a crucial role in a variety of industries. Understanding how riser measurement applies to specific fields can help ensure that you use the correct approach for each system. Let’s explore how riser measurements are applied in construction, plumbing, electrical systems, and HVAC systems.
Riser Measurement in Construction
In the construction industry, riser measurements are vital for integrating essential systems like plumbing, electrical wiring, and HVAC ducts into multi-story buildings. Proper measurement ensures these systems are installed correctly and safely.
- Plumbing Risers: Accurate riser measurement in plumbing ensures that water and waste systems flow properly throughout the building. A plumbing riser typically carries water or waste vertically from one floor to another. Measuring the diameter and height of these risers ensures adequate water pressure and prevents clogs or leaks.
- Electrical Risers: Electrical risers carry wires or cables between floors to distribute electricity safely. Proper measurement is essential for calculating the right cable size and ensuring electrical code compliance. An incorrectly measured riser can lead to power shortages, overheating, or safety hazards.
- HVAC Risers: These risers carry air ducts or ventilation systems between floors to regulate temperature and air quality. Accurate measurement ensures optimal airflow and temperature control, which is essential for comfort and energy efficiency in large buildings.
Key Takeaways for Construction:
- Ensuring risers are the correct size, positioned well, and placed with sufficient spacing can prevent costly mistakes during construction.
- Measurement mistakes can delay projects, impact system efficiency, and even require costly rework.
Riser Measurement in Plumbing Systems
Plumbing riser systems are used to transport water and waste vertically through buildings. Accurate measurement of plumbing risers is essential for ensuring the system works as designed.
- Height Measurement: The height of a plumbing riser affects water pressure and flow rate. If a riser is too small or too short, it can lead to poor water pressure or even blockages.
- Diameter Measurement: The diameter of the pipe is crucial for maintaining adequate water flow. Larger pipes allow for higher flow, while smaller pipes can cause blockages and poor water pressure.
- Spacing: When multiple risers are placed in the same area, proper spacing is essential to prevent interference and allow for easy maintenance.
Example: When installing plumbing risers in a high-rise building, it’s important to measure the height correctly. If the riser doesn’t reach the upper floors, water pressure could be too low to service the highest units effectively.
Riser Measurement in Electrical Systems
In electrical systems, riser cables are used to carry electrical wiring from one floor to another in buildings, ensuring that electricity is distributed correctly to each floor. Accurate riser measurement ensures that cables are the correct size and are installed with enough clearance for safety.
- Cable Size: The diameter of the riser cable needs to be measured accurately to ensure it can carry the required current without overheating.
- Vertical Spacing: For safety, electrical risers should be spaced adequately from walls or other electrical systems to prevent interference and to comply with building codes.
- Safety Considerations: If riser cables are not measured correctly, they can lead to electrical faults, short circuits, or even fires.
Example: In a commercial building, a riser cable that is too small could result in power shortages to the upper floors or cause overheating in the system.
Riser Measurement in HVAC Systems
In HVAC systems, risers are used to carry air ducts or ventilation systems between floors. Proper riser measurements in HVAC installations are crucial for ensuring proper airflow, temperature regulation, and system efficiency.
- Duct Size: The diameter of HVAC ducts should be measured to ensure the airflow is sufficient for the space it serves. Incorrect sizing can lead to poor air quality and temperature regulation.
- Riser Height: The height of a riser in HVAC systems is crucial to ensure that air flows freely from one floor to another. If the riser is not high enough or has a blockage, it can lead to inefficient airflow and higher energy costs.
- Spacing and Alignment: Ensuring that HVAC risers are spaced correctly and aligned helps maintain consistent airflow, preventing air pressure issues and promoting energy efficiency.
Example: An improperly sized HVAC riser in a multi-story office building could result in temperature imbalances, leaving some floors too hot while others remain too cold.
Riser Measurement Standards and Guidelines
Riser measurement is not only about getting the right numbers but also adhering to the relevant standards and guidelines. These rules ensure that risers are measured and installed in a way that is safe, efficient, and code-compliant.
Industry Standards for Riser Measurements
Different industries have specific regulations and standards for riser measurements. For example:
- Plumbing Codes: In the U.S., the International Plumbing Code (IPC) provides guidelines on the minimum required sizes and spacing for plumbing risers.
- Electrical Codes: The National Electrical Code (NEC) outlines requirements for the size and installation of electrical risers to prevent overheating and ensure safety.
- HVAC Standards: The ASHRAE (American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers) provides guidelines on the proper sizing of ducts and risers to maintain efficient airflow.
Best Practices for Riser Measurement
To ensure that your riser measurements meet industry standards and are as accurate as possible, follow these best practices:
- Use the Right Tools: For accurate measurements, always use the appropriate measuring tools (laser measure, tape measure, caliper).
- Check Local Codes: Be sure to check local building codes or standards for specific requirements related to riser measurements.
- Double-Check Measurements: Always measure twice to avoid costly errors and rework later.
The Importance of Accurate Riser Measurement
Accurate riser measurement is crucial for the safe and efficient operation of plumbing, electrical, and HVAC systems. By understanding what riser measurement is, how to do it correctly, and the common mistakes to avoid, you can ensure that your systems are built to last and function properly.
Remember, proper riser measurement not only affects the performance and efficiency of your systems but also impacts safety and compliance with local codes and regulations. Whether you’re working in construction, plumbing, electrical, or HVAC fields, investing time and effort into getting your riser measurements right will pay off in the long run, preventing costly repairs and ensuring smooth operation for years to come.
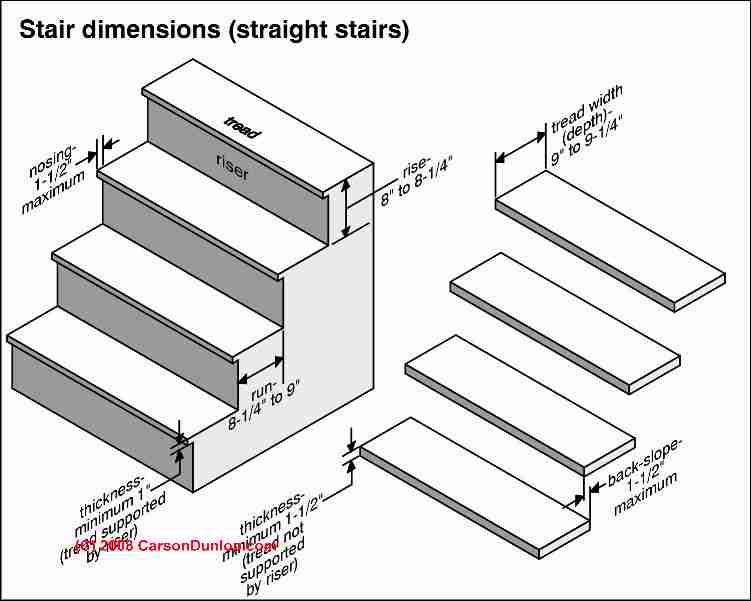
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Riser Measurement
What Is the Difference Between a Riser and a Branch Line?
A riser refers to any vertical component used to transport materials such as water, electricity, or air from one floor to another in a building. In contrast, a branch line is typically a horizontal or sloped line that connects individual components to a central system, like connecting a plumbing fixture to the main water line.
- Riser: Vertical line used to transport materials up or down between floors.
- Branch Line: Horizontal or sloped line that branches off from a main riser or trunk line.
While both risers and branch lines are part of a system’s infrastructure, risers typically deal with vertical transportation, while branch lines distribute the flow horizontally.
How Can I Measure a Riser for HVAC Systems?
When measuring a riser for an HVAC system, you must consider several factors, including the height, diameter, and airflow requirements:
- Height: Measure the vertical distance the ductwork will cover. The height determines how far the air will travel and whether additional booster fans are needed to maintain airflow.
- Diameter: The size of the ductwork affects the volume of air that can be moved through the system. Larger ducts allow for higher airflow, reducing resistance.
- Alignment: Ensure that the ductwork runs straight and vertical. A misaligned riser can lead to poor airflow and energy inefficiency.
- Spacing: Proper spacing between ducts and other risers ensures that airflow isn’t obstructed and that access for maintenance is easy.
Make sure to account for any material expansion or contraction based on temperature changes, especially in larger systems.
Can I Use the Same Measurement Methods for All Types of Risers?
While the basic principles of riser measurement—such as determining height, diameter, and spacing—apply across plumbing, electrical, and HVAC systems, the measurement methods may vary depending on the material and purpose of the riser:
- Plumbing Risers: Focus on water flow, so pipe diameter and height are critical. Use tools like tape measures and calipers for precise measurements.
- Electrical Risers: Emphasize the ability to carry electrical cables safely, so cable size, spacing, and safety clearances are key. Use a laser measure for height and a caliper for diameter, ensuring the right sizing for the cable.
- HVAC Risers: Focus on airflow and temperature regulation. Measure duct size and height, and ensure proper spacing for air circulation. Tools like a duct calculator may also help when sizing ducts.
In all cases, remember that specific industry codes or local regulations may influence how risers should be measured and installed, so always check those before proceeding.
What Are Some Common Problems in Riser Measurement and How Can I Prevent Them?
There are a few common problems that may arise when measuring risers:
- Misaligned Measurements: When risers are not measured from the correct points, misalignment occurs. To avoid this, always use a level or plumb line to ensure the riser is perfectly vertical.
- Incorrect Sizing: A common issue in riser measurement is the wrong diameter or height, leading to poor performance. Always check the required specifications based on the system’s needs and use a reliable measuring tool.
- Inadequate Spacing: Not leaving enough space between multiple risers can lead to overcrowding, reducing efficiency. Always ensure that risers are placed with proper spacing according to system requirements and building codes.
Solution: To prevent these issues, double-check your measurements before installation, use the correct tools, and consult relevant codes or guidelines. Taking the time to do it right the first time can save you a lot of trouble later.
How Do I Know if My Riser Measurements Are Code-Compliant?
To ensure that your riser measurements comply with building codes, follow these steps:
- Consult Industry Standards: Each type of riser (plumbing, electrical, HVAC) will have its own set of standards that must be followed. For example, plumbing riser measurements must adhere to codes like the International Plumbing Code (IPC), while electrical risers need to comply with the National Electrical Code (NEC).
- Review Local Codes: Local jurisdictions may have additional requirements beyond the national standards, so it’s important to verify the specific codes applicable to your location.
- Check Manufacturer Specifications: For certain riser systems, particularly HVAC or electrical risers, manufacturers will provide detailed specifications on the dimensions and spacing required for their products.
- Use Approved Calculation Methods: Some systems, such as HVAC ductwork, may require specific calculation methods for sizing. Consult the ASHRAE (American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers) or similar industry bodies for approved calculation standards.
What Is the Role of a Riser in Building Design?
Risers are integral components in building design because they facilitate the vertical movement of essential services. Without risers, it would be difficult to provide consistent water flow, electricity, or air quality across multiple levels of a building.
Key Functions of Risers in Building Design:
- Water Distribution: Plumbing risers ensure that water is supplied efficiently to every floor.
- Power Distribution: Electrical risers carry power to different parts of the building, ensuring consistent and safe electrical supply.
- Airflow Regulation: HVAC risers are responsible for regulating temperature and air quality, ensuring that ventilation systems function properly in multi-story buildings.
Proper riser measurement ensures that these services are distributed effectively and without interruption.
Final Thoughts on Riser Measurement
Riser measurement is a critical aspect of building design and system installation. Whether you’re working on plumbing, electrical, or HVAC systems, getting the measurements right is essential for ensuring that systems are safe, efficient, and effective. From understanding the key dimensions of a riser (height, diameter, spacing) to choosing the right tools and adhering to industry standards, precision in riser measurement is crucial for the successful operation of any building system.